
Sponsored by China Society of Automotive Engineers
Published by AUTO FAN Magazine Co. Ltd.


Automotive Engineering ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (8): 1573-1587.doi: 10.19562/j.chinasae.qcgc.2025.08.013
Chao Wang1,Wanyuan Yu2( ),Aiguo Cheng1,Zhicheng He1,Tao Chen1
),Aiguo Cheng1,Zhicheng He1,Tao Chen1
Received:2025-01-07
Revised:2025-02-19
Online:2025-08-25
Published:2025-08-18
Contact:
Wanyuan Yu
E-mail:ywy196364@126.com
Chao Wang,Wanyuan Yu,Aiguo Cheng,Zhicheng He,Tao Chen. Research on the Forming Quality and Mechanical Properties of Flat-Surface-Overlapped Self-piercing Riveted Aluminum Alloy Joints[J].Automotive Engineering, 2025, 47(8): 1573-1587.
"
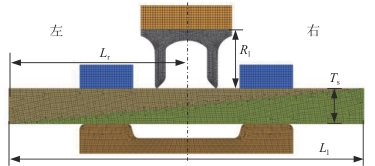 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 研究对象 | Ll/mm | Lr/mm | Ts/mm | Rl/mm | 研究对象 | Ll/mm | Lr/mm | Ts/mm | Rl/mm |
| 搭接长度 | 20.0 | 10.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 板材厚度 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 2.0 | 5.0 |
| 25.0 | 12.5 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 2.5 | 5.0 | ||
| 30.0 | 15.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | ||
| 35.0 | 17.5 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 3.5 | 5.0 | ||
| 40.0 | 20.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 | ||
| 45.0 | 22.5 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 4.5 | 5.0 | ||
| 50.0 | 25.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | ||
| 铆接位置 | 40.0 | 10.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 5.5 | 5.0 | |
| 40.0 | 15.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 6.0 | 5.0 | ||
| 40.0 | 20.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 铆钉长度 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | |
| 40.0 | 25.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 3.0 | 4.5 | ||
| 40.0 | 30.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 3.0 | 5.5 | ||
| 40.0 | 35.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 40.0 | 20.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 | ||
| [1] | 郝瀚,王司南,李骁,等. 面向CAFC法规的汽车企业轻量化策略研究[J]. 汽车工程. 2017, 39(1): 1-8. |
| HAO H, WANG S N, LI J, et al. A research on CAFC regulation-oriented lightweighting strategy for automotive manufacturers[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2017, 39(1): 1-8. | |
| [2] | LI J, WANG L, CHEN Y, et al. Research and application of lightweight index for passenger cars [J]. Automotive Innovation, 2020, 3(3): 270-279. |
| [3] | YANG H, REN Y. Crashworthiness design of CFRP/AL hybrid circular tube under lateral crushing [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2023, 186: 110669. |
| [4] | JIANG H Y, JI Y, HU Y S, et al. Interfacial design and flexural property of CFRP/aluminum-honeycomb sandwich with Aramid-pulp micro/nano-fiber interlays [J]. Composite Structures, 2022, 289: 115486. |
| [5] | 陈静, 徐森, 刘震, 等. 基于碰撞安全性的铝合金吸能盒轻量优化[J]. 汽车工程, 2021, 43(2): 241-247. |
| CHEN J, XU S, LIU Z, et al. Lightweight optimization of aluminum alloy energy absorbing box for crash safety[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2021, 43(2): 241-247. | |
| [6] | CETIN E, BAYKASOĞLU C. Crashworthiness of graded lattice structure filled thin-walled tubes under multiple impact loadings [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2020, 154: 106849. |
| [7] | WESSELMECKING S, KREINS M, DAHMEN M, et al. Material oriented crash-box design-combining structural and material design to improve specific energy absorption [J]. Materials & Design, 2022, 213: 110357. |
| [8] | 刘波, 唐永鑫, 伍毅, 等. 一体压铸铝合金车身结构件的轻量化设计研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2024, 46(12): 2154-2163. |
| LIU B, TANG Y X, WU Y, et al. Study on lightweight design of integrated mega-casting aluminum alloy vehicle body components[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2024, 46(12): 2154-2163. | |
| [9] | AKAR M A, KUMLU U, YıLDıZHAN Ş. Numerical investigation of crash behavior of vehicle side door beams under high-speed pole side impacts [J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2023, 237(14): 3408-3418. |
| [10] | ZHANG W, XU J. Advanced lightweight materials for automobiles: a review [J]. Materials & Design, 2022, 221: 110994. |
| [11] | 任宝凯, 周亢, 王刚. 超声振动辅助铝/钢电阻点焊接头形成机理研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2024, 60(22): 139-152. |
| REN B K, ZHOU K, WANG G. Exploring the formation mechanism of aluminum/steel resistance spot welding joint assisted by ultrasonic vibration[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2024, 60(22): 139-152. | |
| [12] | 慕文龙, 那景新, 秦国锋, 等. 极限温度下的CFRP-铝合金粘接接头耐久性研究[J].汽车工程, 2020, 42(7):985-992. |
| MU W L, NA J X, QIN G F, et al. Study on durability of adhesively bonded CFRP-aluminum alloy joints exposed to extreme temperatures[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2020, 42(7):985-992. | |
| [13] | LI D, CHRYSANTHOU A, PATEL I, et al. Self-piercing riveting-a review [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2017, 92(5-8): 1777-1824. |
| [14] | JIANG H, GAO S, LI G, et al. Structural design of half hollow rivet for electromagnetic self-piercing riveting process of dissimilar materials [J]. Materials & Design, 2019, 183: 108141. |
| [15] | KARIM M, JEONG T, NOH W, et al. Joint quality of self-piercing riveting (SPR) and mechanical behavior under the frictional effect of various rivet coatings [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2020, 58: 466-477. |
| [16] | UHE B, MESCHUT G. Advanced self-piercing riveting of ultra-high-strength steel through rivets with modified material properties [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2024, 125: 354-363. |
| [17] | LI Y, LIM Y C, FENG Z. Effect of die design on microstructure and mechanical joint strength in friction self-piercing riveted AA7055-T76 and AA7055-T76 [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2024, 124: 119-130. |
| [18] | MA Y, NIU S, SHAN H, et al. Impact of stack orientation on self-piercing riveted and friction self-piercing riveted aluminum alloy and magnesium alloy joints [J]. Automotive Innovation, 2020, 3(3): 242-249. |
| [19] | WANG C, DU Z, CHENG A, et al. Influence of process parameters and heat treatment on self-piercing riveting of high-strength steel and die-casting aluminium [J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2023, 26: 8857-8878. |
| [20] | DUAN J, CHEN C. Effect of edge riveting on the failure mechanism and mechanical properties of self-piercing riveted aluminium joints [J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2023, 150: 107305. |
| [21] | XIE Z, ZHANG A, YAN W, et al. Study on shear performance and calculation method for self-pierce riveted joints in galvanized steel sheet [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2021, 161: 107490. |
| [22] | WANG C, YU W, CHENG A, et al. Effect of process parameters on joint quality and mechanical properties of local-thickened self-piercing riveted steel and die-casting aluminum joints [J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2024, 132: 5945-5964. |
| [23] | 廖品翔, 林建平, 闵峻英, 等. 下板厚度对钢/铝自冲铆接接头单搭剪切强度的影响[J].锻压技术, 2022, 47(7): 145-153. |
| LIAO P X, LIN J P, MIN J Y, et al. Influence of lower plate thickness on single lap shear strength of joint in steel and aluminum self-piercing riveting[J]. Forging & Stamping Technology, 2022, 47(7): 145-153. | |
| [24] | JIN J, LIAO Y, QIN J, et al. A novel electromagnetic self-pierce upsetting riveting with flat die for joining ultra-high strength steel and aluminum structures [J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2024, 336: 118691. |
| [25] | SHI C, LI H, CHEN C, et al. Experimental investigation of the flat clinch-rivet process [J]. Thin-Walled Structures, 2022, 171: 108612. |
| [26] | REN X, CHEN C. Research on mechanical clinching process for dissimilar aluminum alloy sheets with inclined surface [J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2023, 89: 362-370. |
| [1] | Jun Wang,Chenghao Ma,Zongxuan Shen,Bobin Xing,Yong Xia. Virtual Simulation Research on Crash Safety of Electric Vehicles Under Side Pole Impact [J]. Automotive Engineering, 2025, 47(6): 1095-1102. |
| [2] | Chunlong Ma,Wenjun Xia,Shengguo Li,Yanyu Guo,Qingyuan Su. Research on Vehicle Frame Lightweight Based on the IHHO Algorithm [J]. Automotive Engineering, 2025, 47(5): 992-1006. |
| [3] | Hengfeng Yin,Dang Lu,Haitao Min,Haidong Wu,Yandong Zhang. Study on the Influence of Inclination Angle on the Mechanical Characteristics of Tire Turn-Slip [J]. Automotive Engineering, 2025, 47(2): 342-355. |
| [4] | Dayong Wang,Junjia Cui,Shaoluo Wang,Shuhao Wang,Hao Jiang,Guangyao Li. Research on the Mechanical Properties and Process Parameter Influence of BFRP/AA5052 Adhesive Joints [J]. Automotive Engineering, 2025, 47(2): 356-366. |
| [5] | Chenghao Ma,Jonghyeon Shin,Jun Wang,Wenhong Ao,Bobin Xing,Yong Xia. Fast Prediction of Battery Pack Safety Under Side Pole Collision [J]. Automotive Engineering, 2025, 47(1): 117-126. |
| [6] | Ying Zhao,Jibo Hao,Keming Zhou,Jianfeng Hu,Yicheng Wang,Yueqiang Wang. Mechanical Properties of Double-arrow Non-pneumatic Tires Under the Condition of Unstructured Road [J]. Automotive Engineering, 2025, 47(1): 149-160. |
| [7] | Daolin Deng. Study on Forming Performance of Aluminum-Plastic Film for Pouch Lithium-Ion Batteries [J]. Automotive Engineering, 2024, 46(7): 1157-1166. |
| [8] | Lijun Qian,Luxin Yu,Xianguang Gu,Wenyu Liang. Crushing Analysis and Interval Optimization Design for Multi Cell Aluminum Alloy Thin-Walled Tubes [J]. Automotive Engineering, 2024, 46(7): 1323-1334. |
| [9] | Chao Wang,Ming Li,Aiguo Cheng,Zhicheng He,Wanyuan Yu. Lightweight Design of Material-Structure for Steel-Aluminum Hybrid Cab [J]. Automotive Engineering, 2024, 46(4): 735-744. |
| [10] | Bo Liu,Yongxin Tang,Yi Wu,Ziyang Wang,Qin Yang,Tiegang Hu,Xiaomin Xu. Study on Lightweight Design of Integrated Mega-casting Aluminum Alloy Vehicle Body Components [J]. Automotive Engineering, 2024, 46(12): 2154-2163. |
| [11] | Weihe Zeng, Ligang Gou, Yu Luo, Jun Zhang, Huihong Liao. Fatigue Simulation and Experimental Study of Super-size Integral Die Casting Aluminum Alloy Rear End Body [J]. Automotive Engineering, 2023, 45(7): 1263-1275. |
| [12] | Dengfeng Wang, Chunda Lu, Hongyu Liang. Multi-objective Optimization Design of Induction Groove for Aluminum/CFRP Hybrid Tube Under Multi-angle Compression Condition [J]. Automotive Engineering, 2023, 45(7): 1286-1298. |
| [13] | Yang Zhao,Kang Ye,Hanqiao Sun,Zunyan Hu,Liangfei Xu,Jianqiu Li,Minggao Ouyang. Study on the Performance and Safety of Aluminum Matrix Composite for Hydrogen Production [J]. Automotive Engineering, 2022, 44(5): 730-735. |
| [14] | Shijie Ruan,Hangjie Su,Haiyan Li,Shihai Cui,Lijuan He,Lü Wenle. Injury Assessment of Three-Year-Old Child Occupant in Frontal 100% Overlap Rigid Barrier Crash Test Simulation [J]. Automotive Engineering, 2022, 44(3): 403-411. |
| [15] | Mingjun Zhang,Xiong Li,Heqing Li,Chenxi Li,Jian Zhang,Bo Cheng,Kaiming Wang,Cong Mao,Yongle Hu. Influence of Nanosecond Pulsed Laser Cleaning on Laser Welding Quality of AZ31B Magnesium Alloy [J]. Automotive Engineering, 2022, 44(11): 1786-1796. |
|
||