

汽车工程 ›› 2024, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (2): 187-200.doi: 10.19562/j.chinasae.qcgc.2024.02.001
• • 下一篇
胡林1,2,谷子逸1,王丹琦1,2( ),王方1,2,邹铁方1,2,黄晶3
),王方1,2,邹铁方1,2,黄晶3
收稿日期:2023-06-19
修回日期:2023-07-27
出版日期:2024-02-25
发布日期:2024-02-23
通讯作者:
王丹琦
E-mail:danqi_wang@csust.edu.cn
基金资助:
Lin Hu1,2,Ziyi Gu1,Danqi Wang1,2( ),Fang Wang1,2,Tiefang Zou1,2,Jing Huang3
),Fang Wang1,2,Tiefang Zou1,2,Jing Huang3
Received:2023-06-19
Revised:2023-07-27
Online:2024-02-25
Published:2024-02-23
Contact:
Danqi Wang
E-mail:danqi_wang@csust.edu.cn
摘要:
在汽车产业电动化和智能化进程中,汽车安全测试评价技术也从单纯被动安全向主被动安全融合方向延伸和扩展。本文从车内乘员保护、车外弱势道路使用者保护与主动安全三方面,深入对比分析了全球主流汽车安全测评规程的差异,总结了针对各测评工况的车辆安全开发技术要点,探讨了新能源与智能网联汽车安全测评规程的发展趋势。研究认为,主流汽车安全测评规程在被动安全评价方面越来越严格,主动安全测评工况比重在逐步增加,未来测评规程的发展重心将集中于主被动安全融合及针对复杂工况的虚拟测评两方面。此外,针对新能源汽车的电池安全测试已相对完善,未来研究重点可向电控系统测试、底盘稳定性测试和充换电设施与配套设备统一标准化认证等方向拓展;而构建合理、可靠的智能网联汽车OTA(over the air)测试、HMI(human machine interface)安全性和舒适性等测评方法,在中长期内将成为行业关注的重难点问题,且可借助自动驾驶模拟器等工具搭建虚实结合的复合测评体系。
胡林,谷子逸,王丹琦,王方,邹铁方,黄晶. 汽车安全性测评规程现状及趋势展望[J]. 汽车工程, 2024, 46(2): 187-200.
Lin Hu,Ziyi Gu,Danqi Wang,Fang Wang,Tiefang Zou,Jing Huang. Current Status and Trend of Automotive Safety Procedures/Programs[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2024, 46(2): 187-200.
表2
典型汽车安全评价规程正面碰撞测试条件"
| 偏置碰撞 | C-NCAP (2021) | C-IASI (2020) | E-NCAP (2023) | US-NCAP (2021) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 碰撞形式示意图 | 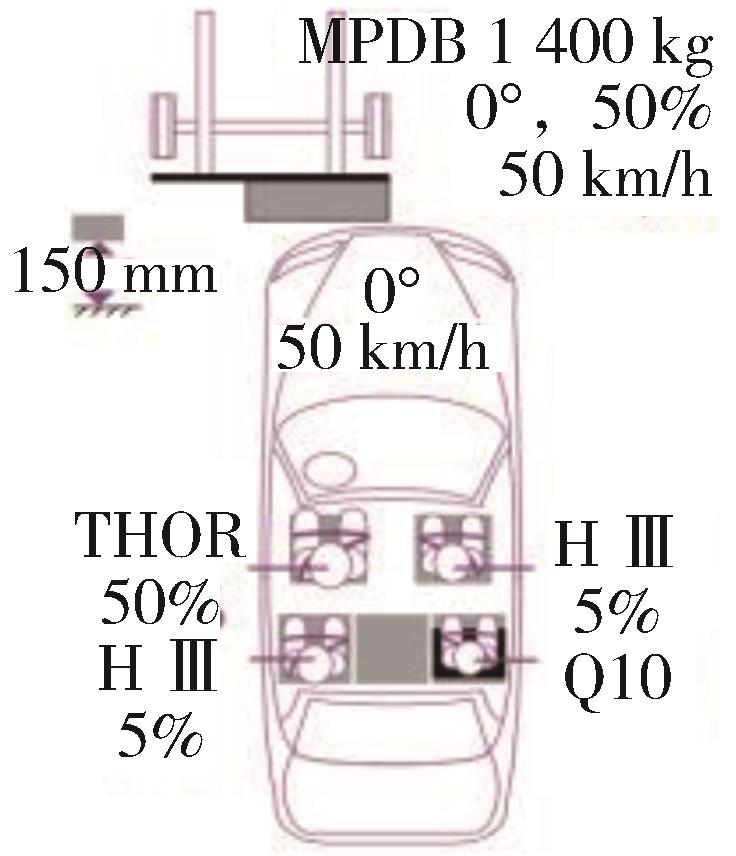 | 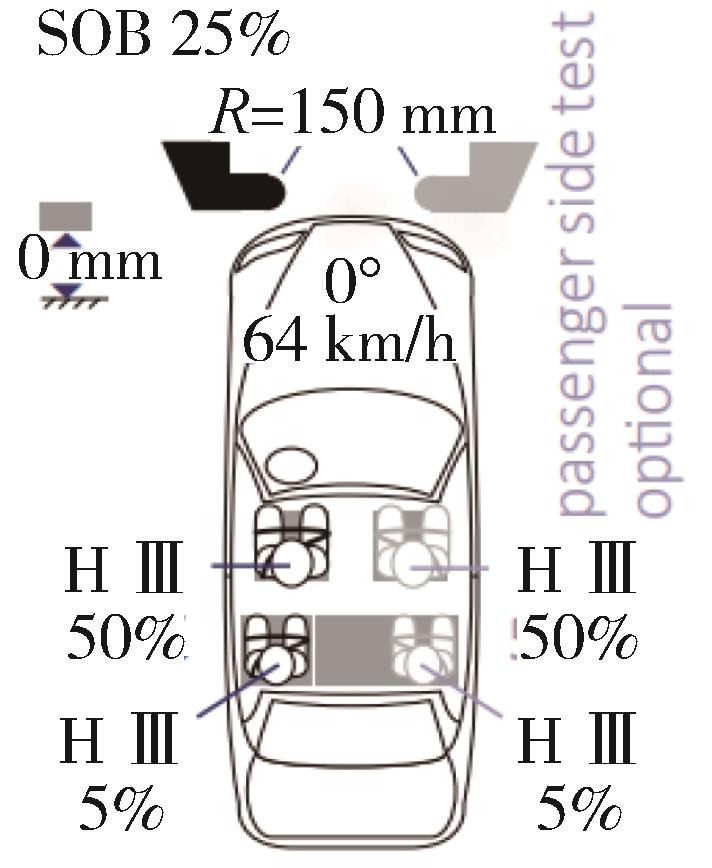 | 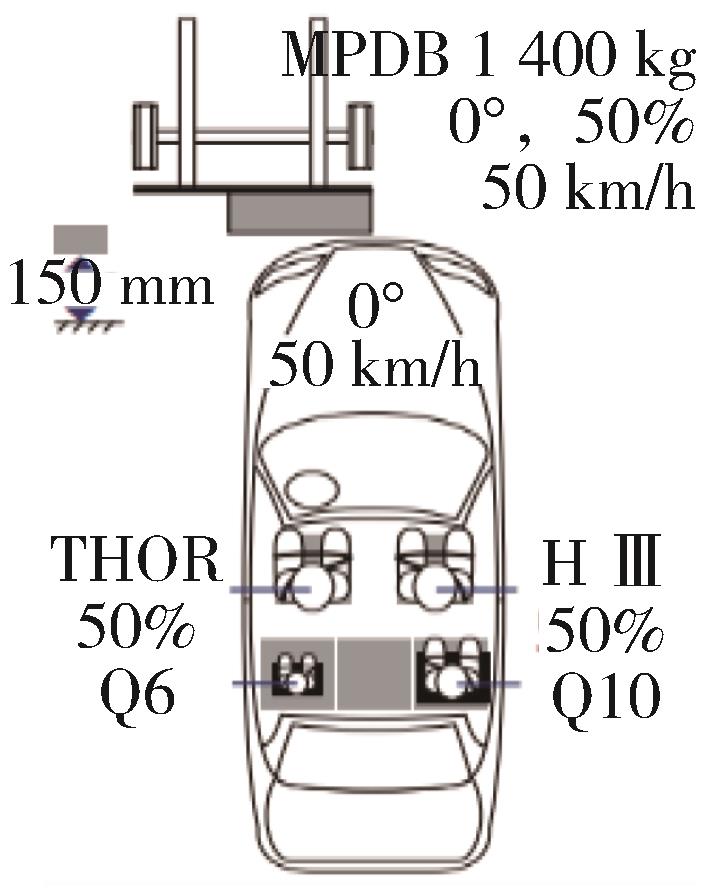 | 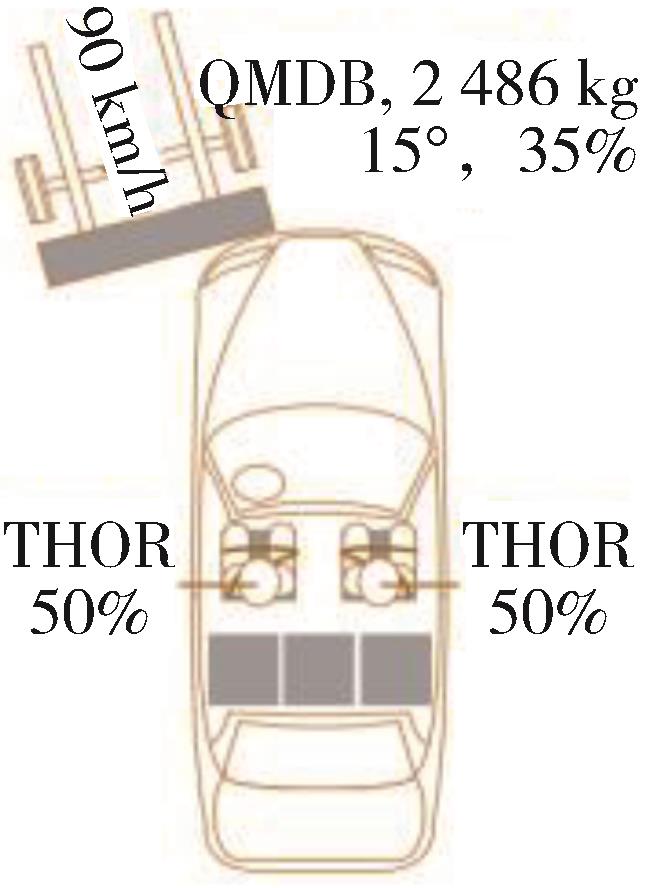 |
| 试验工况 | 正面50%偏置碰撞 MPDB | 正面25%偏置碰撞 SOB | 正面50%偏置碰撞 MPDB | 正面35%斜角碰撞 OMDB |
| 假人选用 | 驾驶员THOR 副驾Hybrid III 后排Hybrid III Q10儿童假人 | 驾驶员Hybrid III 后排左侧Hybrid III | 驾驶员THOR 副驾Hybrid III 后排儿童假人Q10、Q6 | 驾驶员THOR 副驾THOR |
| 假人测点(驾驶员) | THOR | Hybrid III | THOR | 工况尚未正式引入测试 |
碰撞速度/ (km·h-1) | 50 | 64 | 50 | 90 |
| 评价方法 | 对假人各部位受伤情况进行考核评价并有兼容性评价 | 从约束系统和假人运动、假人伤害、车辆结构3个方面进行评价 | 对假人各部位受伤情况进行考核评价并有兼容性评价 | 驾乘人员单独评价,取二者平均值之和做评价结果(100%重叠正面碰撞) |
表3
典型汽车安全测评规程中的侧面碰撞测试工况"
| 侧面碰撞 | C-NCAP(2021) | C-IASI(2020) | E-NCAP(2023) | US-NCAP(2021) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
碰撞形式 示意图 | 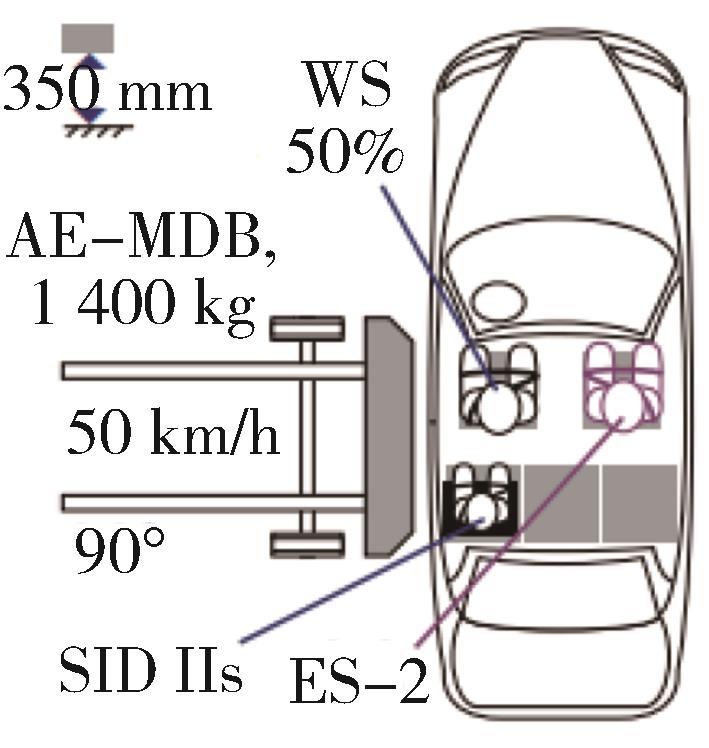 | 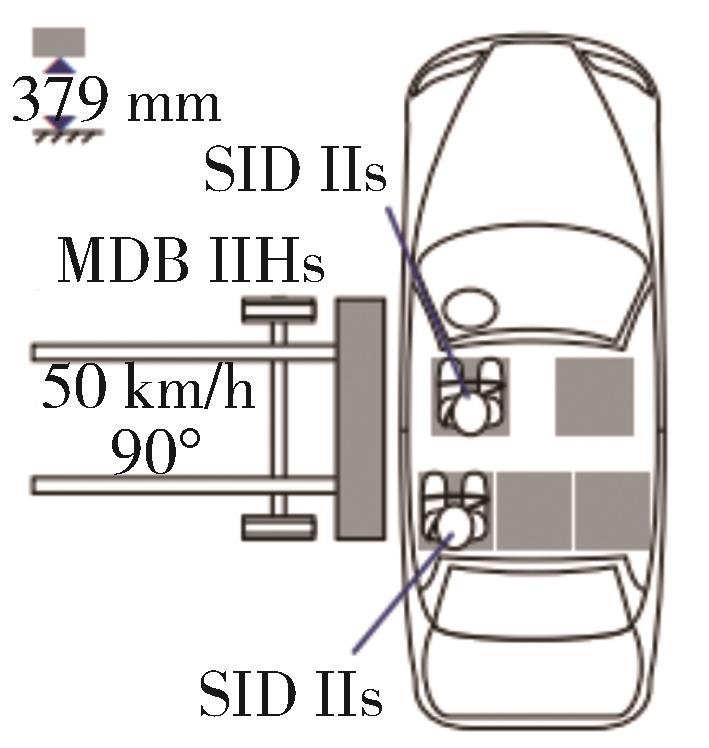 | 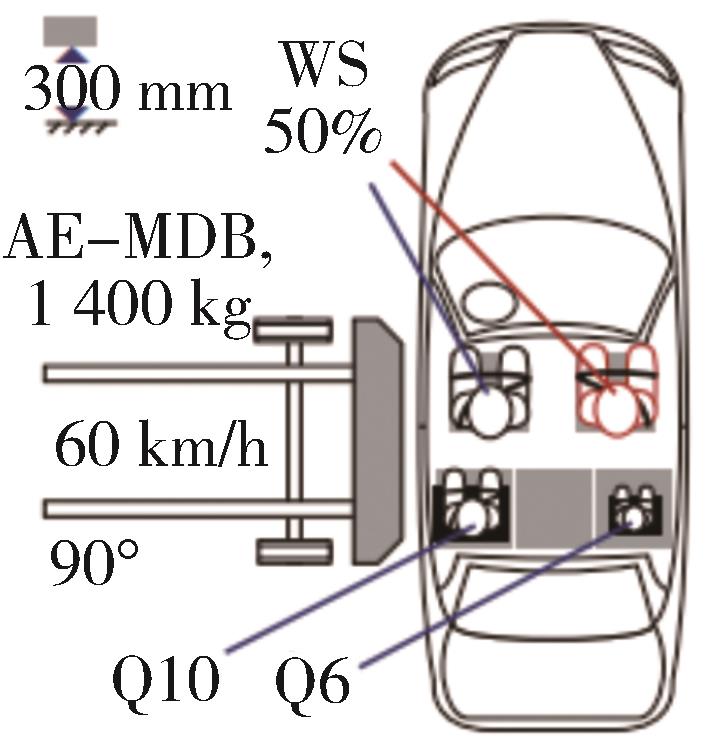 | 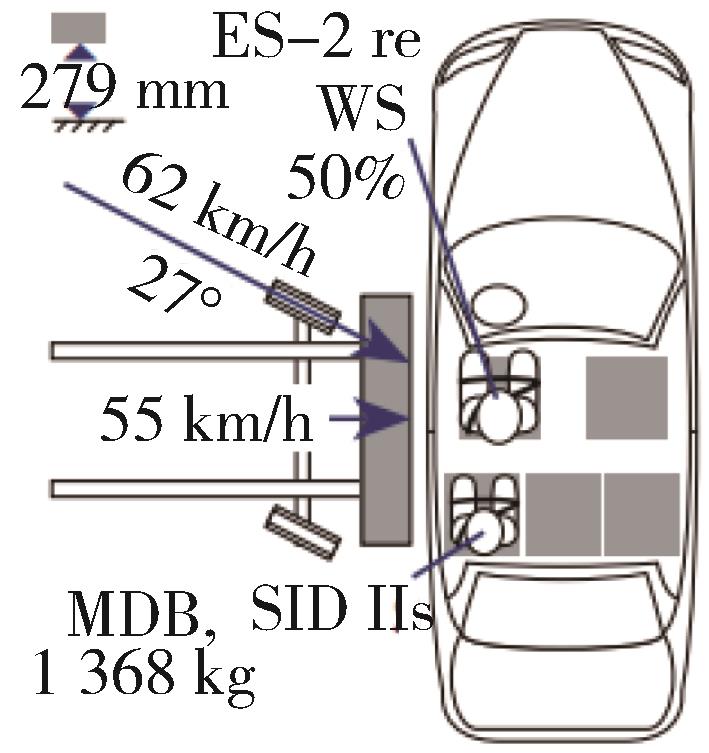 |
| 试验工况 | 1.可移动变形壁障侧碰撞 2.侧面柱碰撞 | 可移动变形壁障侧碰撞 | 1.可移动变形壁障侧碰撞 2.侧面柱碰撞 | 1.可移动变形壁障侧碰撞 2.侧面柱碰撞 |
| 碰撞角度 | 1.90°(侧面碰撞) 2.75°(侧面柱碰撞) | 90°(侧面碰撞) | 1.90°(侧面碰撞) 2.75°(侧面柱碰撞) | 1.90°、27°(侧面碰撞) 2.75°(侧面柱碰撞) |
碰撞速度/ (km·h-1) | 1. 50 2. 32 | 50 | 1. 60 2. 32 | 1. 55、62 2. 32 |
| 假人选用 | 1.驾驶员 World-SID 副驾ES-2,后排左侧 SID-IIs(D版) 2.驾驶员World-SID | 驾驶员侧SID-IIs(D版), 后排左侧SID-IIs型(D版) | 1.驾驶员World-SID 2.前排World-SID (双乘员试验使用2个) | 1.驾驶员ES-2 re, 后排SID-IIs(D版) 2.驾驶员侧SID-IIs(D版) |
假人测点 (驾驶员) | World-SID | SID-IIs:头部和颈部、躯干、骨盆和腿部 | World-SID | ES-2 re:头、胸、腹、骨盆 |
| 壁障质量/kg | 1 400 | 1 500 | 1 400 | 1 368 |
表6
2021版C-NCAP与2023版E-NCAP AEB测试对比"
| 测试项目 | C-NCAP(2021) | E-NCAP(2023) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AEB车对车 | CCRs(接近静止车辆) | AEB | 20-40 km/h 碰撞位置-50%-50% | 10-50 km/h 碰撞位置-50%-50% |
| CCRs(接近静止车辆) | FCW | 50-80 km/h 碰撞位置-50%-50% | 55-80 km/h 碰撞位置-50%-50% | |
| CCRm(接近慢速行驶车辆) | AEB | 30-50 km/h 碰撞位置-50%-50% | 30-80 km/h 碰撞位置-50%-50% | |
| CCRm(接近慢速行驶车辆) | FCW | 60-80 km/h 碰撞位置-50%-50% | ||
| AEB二轮车 | CBNA | AEB | 20-60 km/h 碰撞位置50%,目标15 km/h | 10-60 km/h 碰撞位置50%,目标10-15 km/h |
| CSFA/CBFA | AEB | 30-60 km/h 碰撞位置50%,目标20 km/h | 10-60 km/h 碰撞位置50%,目标20 km/h | |
| CBLA | AEB | 20-60 km/h 碰撞位置50%,目标15 km/h | 25-60 km/h 碰撞位置50%,目标15 km/h | |
| CBLA | FCW | 50-80 km/h 碰撞位置25%,目标15 km/h | 50-80 km/h 碰撞位置25%,目标20 km/h | |
| AEB行人 | CPNA | AEB | 20-60 km/h 碰撞位置25%、50%,目标5 km/h | 10-60 km/h 碰撞位置25%、75%,目标5 km/h |
| CPFA | AEB | 20-60 km/h 碰撞位置25%、75%,目标6.5 km/h | 10-60 km/h 碰撞位置50%,目标8 km/h | |
| CPLA | AEB | 20-60 km/h 碰撞位置25%、50%,目标5 km/h | 20-60 km/h 碰撞位置50%,目标5 km/h | |
| CPLA | FCW | 50-80 km/h 碰撞位置25%,目标5 km/h | 50-80 km/h 碰撞位置25%,目标5 km/h | |
表7
2021版C-NCAP和2023版E-NCAP辅助驾驶测试项目"
| 测试项目 | LDW | LKA | BSD | SAS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全称 | Lane Departure Warning 车道偏离预警 | Lane Keeping Assist 车道保持辅助 | Blind-Spot Detection 盲点监测 | Speed Assist System 速度辅助系统 |
C-NCAP(2021) 试验标准 | 车速80 km/h 向左向右以0.6、0.7 m/s偏离实线 | 车速80 km/h 虚实线左右侧以0.2-0.5 m/s偏离 | 测试车和目标车都是50 km/h,并道接近用60-70 km/h超越试验车辆 | 测试车对40和60 km/h限速标识牌进行识别并报警 |
E-NCAP(2023) 试验标准 | 车辆以虚实线左右侧以0.6-1.0 m/s偏离 | 车辆以虚实线左右侧以0.2-0.6 m/s偏离 | 试验车辆72 km/h,目标车辆以80 km/h超越试验车辆 | 准确识别限速标识牌、道路特征和局部危险并发出警告或采取措施 |
| 1 | ZOU Y, ZHANG Y, CHENG K. Exploring the impact of climate and extreme weather on fatal traffic accidents[J]. Sustainability, 2021, 13(1): 390. |
| 2 | 中华人民共和国统计局.中国统计年鉴[M].北京:中国统计出版社, 2019. |
| Statistics Administration of the People's Republic of China. China statistical yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2019. | |
| 3 | C⁃NCAP管理中心.C⁃NCAP管理规则(2021版)[S].天津:中国汽车技术研究中心,2020. |
| C⁃NCAP Management Center. C⁃NCAP management rules (2021 edition) [S]. Tianjin: China Automotive Technology and Research Center,2020. | |
| 4 | Safety companion 2022 [Z]. Germany: Carhs, 2022. |
| 5 | Euro NCAP Rating Group. Euro NCAP (2023) [EB/OL]. [2022-05-18].https://www.euroncap.com/en/for-engineers/protocols/. |
| 6 | 中国保险汽车安全指数管理中心.中国保险汽车安全指数管理办法(2020版)[S]. 北京: 中国保险汽车安全指数管理中心,2021. |
| China Insurance Auto Safety Index Management Center. Measures for the administration of insurance automobile safety index in China (2020 edition) [S]. Beijing: Insurance Auto Safety Index Management Center of China, 2021. | |
| 7 | AHANGARNEJAD A H, RADMEHR A, AHNADIAN M. A review of vehicle active safety control methods: from antilock brakes to semiautonomy[J]. Journal of Vibration and Control, 2021, 27(15-16): 1683-1712. |
| 8 | Euro NCAP 2030 Vison. A safer future for mobility [EB/OL]. [2022-11-9]. http://www.euroncap.com. |
| 9 | 黄慧丽,王刚.主流汽车安全评价体系发展研究[J].标准科学,2019(4):61-65,77. |
| HUANG H L, WANG G. Research on the development of mainstream automobile safety evaluation system[J]. Standard Science, 2019(4):61-65,77. | |
| 10 | 杨帅,张金换,钱占伟,等.汽车安全多领域融合的研究与展望[J].汽车安全与节能学报,2022,13(1):29-47. |
| YANG S, ZHANG J H, QIAN Z W, et al. Research and prospect of multi-domain integration of automotive safety[J]. Journal of Automotive Safety and Energy, 2022, 13(1): 29-47. | |
| 11 | 郑捷,彭炫权,杨军,等.MPDB 工况下碰撞兼容性的基本 问题与车体设计原则[J].中国公路学报,2022,35(4):313-324. |
| ZHENG J,PENG X Q,YANG J, et al. The basic problems of collision compatibility and body design principles under MPDB working conditions[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2022,35(4): 313-324. | |
| 12 | REICHERT R, KAN C D. Effect of impact configuration variance in oblique frontal offset tests on driver and passenger injury risk[C]. IRCOBI Conference, 2019. |
| 13 | 刘明,商博,赵清江.整车MPDB试验中THOR假人损伤的研究[J].汽车工程,2021,43(8):1223-1227. |
| LIU M, SHANG B, ZHAO Q J. Study on damage of THOR dummy in vehicle MPDB test[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2021, 43(8): 1223-1227. | |
| 14 | 陆凯.汽车被动安全系统技术发展研究及应对[J].上海汽车,2022(9):35-43,48. |
| LU K. Research and response to the development of automotive passive safety system technology[J]. Shanghai Auto, 2022(9): 35-43,48. | |
| 15 | 公安部交通管理局. 中国人民共和国道路交通事故统计年报(2020年度)[R]. 北京: 公安部交通管理局,2020. |
| Traffic Management Bureau of the Ministry of Public Security. Annual report on road traffic accident statistics of the Chinese People's Republic of China (2020)[R]. Beijing: Traffic Management Bureau of the Ministry of Public Security,2020. | |
| 16 | 中国汽车工程研究院.中国汽研推出首款中国特色侧碰壁障AC-MDB [EB/OL].[2021-05-06]. https://www.auto-testing.net/news/show-110664.html. |
| China Automotive Engineering Research Institute. CAERI launches the first Chinese characteristic side barrier AC-MDB[EB/OL].[2021-05-06].https://www.auto-testing.net/news/show-110664.html. | |
| 17 | 郝琪,李海伦,崔宏伟,等.考虑侧面柱碰的电动汽车车门多学科优化设计[J].汽车安全与节能学报,2020,11(3):314-321. |
| HAO Q, LI H L, CUI H W, et al. Multidisciplinary optimization design of electric vehicle door considering side column collision[J]. Journal of Automotive Safety and Energy, 2020, 11(3): 314-321. | |
| 18 | 唐涛,张维刚,陈鼎,等.侧面柱碰撞条件下轿车车门抗撞性优化设计[J].中国机械工程,2016,27(2):278-283. |
| TANG T, ZHANG W G, CHEN D, et al. Optimization design of crashworthiness of car door under side column collision[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 27(2): 278-283. | |
| 19 | 陈涛,李宁宁,李卓,等.侧面柱碰撞条件下电动汽车电池系统结构优化[J].中国机械工程,2020,31(9):1021-1030. |
| CHEN T, LI N N, LI Z, et al. Structural optimization of electric vehicle battery system under side column collision conditions[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 31(9): 1021-1030. | |
| 20 | PARK Y, OH Y K. Estimation of WorldSID thorax kinematics using multiple 3-axis accelerometers[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 2019, 33: 5739-5746. |
| 21 | 刘磊, 朱海涛, 李充, 等. WorldSID50百分位男性假人研究 [J]. 天津科技, 2014, 41(8): 50-54. |
| LIU L, ZHU H T, LI C, et al. Study on WorldSID50 percentile male dummies[J]. Tianjin Science and Technology, 2014, 41(8): 50-54. | |
| 22 | 周会锋,李碧浩,王大志.WorldSID 50th 假人与ES-2假人的性能对比分析[J].汽车安全与节能学报,2017,8(3):261-267. |
| ZHOU H F, LI B H, WANG D Z. Comparative analysis of performance of WorldSID 50th dummy and ES-2 dummy[J]. Journal of Automotive Safety and Energy, 2017, 8(3): 261-267. | |
| 23 | PEREZ-RAPELA D, DONLON J P, FORMAN J L, et al. Occupant restraint in far-side impacts: cadaveric and WorldSID responses to a far side airbag [J]. Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 2021, 49(2): 802-811. |
| 24 | PIKORN B, ÖSTH J, BRYNSKOG E, et al. Validation of the SAFER human body model kinematics in far-side impacts [C]. Proceedings of the IRCOBI Conference, 2021. |
| 25 | 张瑞文,周澄靖,陈高军,等. Far-side侧面碰撞研究进展[C].2020中国汽车工程学会年会论文集,2020:563-568. |
| ZHANG R W, ZHOU C J, CHEN G J, et al. Research progress of far-side side collision[C]. Proceedings of the 2020 SAE China Annual Conference, 2020: 563-568. | |
| 26 | 洪亮,刘刚,葛如海.基于12岁儿童损伤阈值的主动式安全气囊多目标优化[J].汽车工程,2021,43(6):861-869. |
| HONG L, LIU G, GE R H. Multi-objective optimization of active airbag based on injury threshold of 12-year-old children [J]. Automotive Engineering, 2021, 43(6): 861-869. | |
| 27 | 孙振东,朱海涛,彭伟强,等.汽车预碰撞制动下乘员离位影响及参数优化分析[J].汽车工程,2023,45(1):112-118. |
| SUN Z D, ZHU H T, PENG W Q, et al. Analysis of occupant departure effect and parameter optimization under pre-collision braking [J]. Automotive Engineering, 2023, 45(1): 112-118. | |
| 28 | 刘刚,洪亮,葛如海.面向“离位”儿童乘员的常开式安全气囊优化设计[J].汽车工程,2022,44(1):94-104. |
| LIU G, HONG L, GE R H. Optimal design of normally open airbag for out-of-position child occupant [J]. Automotive Engineering, 2022, 44(1): 94-104. | |
| 29 | 《中国公路学报》编辑部.中国汽车工程学术研究综述·2017[J].中国公路学报,2017,30(6):1-197. |
| Editorial Board of China Journal of Highway and Transport. Review of academic research in automotive engineering in China 2017[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2017, 30(6): 1-197. | |
| 30 | 李海岩,杨振,贺丽娟,等.全球NCAP行人保护测评的对比研究及展望[J].汽车工程,2021,43(5):730-738. |
| LI H Y, YANG Z, HE L J, et al. Comparative study and prospect of global NCAP pedestrian protection assessment[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2021, 43(5): 730-738. | |
| 31 | C⁃NCAP管理中心.C⁃NCAP管理规则(2018版)[S].天津:中国汽车技术研究中心,2018. |
| C⁃NCAP Management Center. C⁃NCAP management rules (2018 edition) [S]. Tianjin: China Automotive Technology and Research Center, 2018. | |
| 32 | MO F, LUO D, TAN Z, et al. A human active lower limb model for Chinese pedestrian safety evaluation[J]. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2021, 18(4): 872-886. |
| 33 | 孙小光,张二鹏,陈现岭,等.行人安全评估发展趋势及应对策略探讨[J].北京汽车,2018(6):31-34,38. |
| SUN X G, ZHANG E P, CHEN X L, et al. Discussion on the development trend and coping strategy of pedestrian safety assessment[J].Beijing Automotive Engineering, 2018(6): 31-34,38. | |
| 34 | 邹铁方,刘期,刘朱紫,等.真实事故中通过制动控制降低人地碰撞损伤的潜在效益及时空约束[J].机械工程学报,2021,57(22):266-276. |
| ZOU T F, LIU Q, LIU Z Z, et al. The potential benefit of reducing human-ground collision damage through braking control in real accidents and space-time constraints[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 57(22): 266-276. | |
| 35 | 邹铁方,肖璟,胡林,等.轿车-行人事故中人体损伤来源与相关性分析[J].汽车工程,2017,39(7):748-753,747. |
| ZOU T F, XIAO J, HU L, et al. Sources and correlation analysis of human injury in car-pedestrian accident[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2017, 39(7): 748-753,747. | |
| 36 | 胡剑伟. 基于行人头部保护的发动机罩多目标拓扑优化设计[D].长沙:湖南大学,2020. |
| HU J W. Multi-objective topology optimization design of engine hood based on pedestrian head protection[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2020. | |
| 37 | 左培文,张立淼,毕腾飞.汽车行人保护技术发展状况与对策建议[J].汽车制造业,2020(11):34-37. |
| ZUO P W, ZHANG L M, BI T F. Development status and countermeasures of automobile pedestrian protection technology[J]. Automobil Industrie, 2020(11): 34-37. | |
| 38 | SUN C, ZHENG S F, MA Y L, et al. An active safety control method of collision avoidance for intelligent connected vehicle based on driving risk perception[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2021, 32: 1249-1269. |
| 39 | HU L, BAO X Q, WU H Q, et al. A study on correlation of traffic accident tendency with driver characters using in-depth traffic accident data[J]. Journal of Advanced Transportation, 2020, 2020: 1-7. |
| 40 | C⁃NCAP管理中心.C⁃NCAP管理规则(2015版)[S].天津:中国汽车技术研究中心,2015. |
| C⁃NCAP Management Center. C⁃NCAP management rules (2015 edition) [S]. Tianjin: China Automotive Technology and Research Center, 2015. | |
| 41 | Euro NCAP. Euro NCAP AEB C2C Test Protocol (v4.2)[EB/OL].[2023-6-01].https://www.euroncap.com/en/for- engineers/protocols/safety-assist/. |
| 42 | 刘永涛,刘传攀,刘湘安,等.基于自适应采样时间MPC的自动紧急制动系统[J].汽车工程,2023,45(1):32-41. |
| LIU Y T, LIU C P, LIU X A, et al. Automatic emergency braking system based on adaptive sampling time MPC[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2023, 45(1): 32-41. | |
| 43 | 韩勇,李永强,许永虹,等.基于VRUs深度事故重建的AEB效能对头部损伤风险的影响[J].汽车安全与节能学报,2021,12(4):490-498. |
| HAN Y, LI Y Q, XU Y H, et al. Effect of AEB efficacy on head injury risk based on VRUs deep accident reconstruction [J]. Journal of Automotive Safety and Energy, 2021, 12(4): 490-498. | |
| 44 | PAN D, HAN Y, JIN Q Q, et al. Study of typical electric two-wheelers pre-crash scenarios using K-medoids clustering methodology based on video recordings in China[J]. Accident Analysis & Prevention, 2021, 160: 106320. |
| 45 | CHEN Y, BOUKERCHE A. A novel lane departure warning system for improving road safety[C]. ICC 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC). IEEE, 2020: 1-6. |
| 46 | 吴东盛,冯南山,陈芷衡.太阳能儿童车内滞留主动安全防护系统设计与试验研究[J].公路与汽运,2018(1):20-24,28. |
| WU D S, FENG N S, CHEN Z H. Design and experimental study of active safety protection system for solar children's car stay[J]. Highway and Automobile Applications, 2018(1): 20-24,28. | |
| 47 | 黄俊富.全球NCAP主动安全测评体系及测试评价方法[Z]. 2020-05-14. |
| HUANG J F. Global NCAP active safety evaluation system and test evaluation method[Z]. 2020-05-14. | |
| 48 | 汪洪波,夏志,陈无畏.考虑人机协调的基于转向和制动可拓联合的车道偏离辅助控制[J].机械工程学报,2019,55(4):135-147. |
| WANG H B, XIA Z, CHEN W W. Lane departure assist control based on steering and braking extension considering human-machine coordination[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(4): 135-147. | |
| 49 | 武和全,侯海彬,胡林,等.自动驾驶汽车中乘员在不同座椅朝向下的损伤风险及规避策略[J].中国公路学报,2019,32(6):206-215,225. |
| WU H Q, HOU H B, HU L, et al. Injury risk and avoidance strategy of occupants facing downward in different seats in autonomous vehicles[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(6): 206-215,225. | |
| 50 | 马艳. 2023年新能源汽车销量预计达850万辆[N]. 中国工业报,2023-01-13(003). |
| MA Y. In 2023, the sales volume of new energy vehicles is expected to reach 8.5 million units[N]. China Industry News, 2023-01-13(003). | |
| 51 | 周卓斌. 全球电动汽车销量强劲增长[N]. 人民日报,2023-03-01(017). |
| ZHOU Z B. Global electric vehicle sales grow strongly [N]. People's Daily, 2023-03-01(017). | |
| 52 | 陈泽宇,熊瑞,孙逢春.电动汽车电池安全事故分析与研究现状[J].机械工程学报, 2019,55(24):93-104,116. |
| CHEN Z Y, XIONG R, SUN F C. Analysis and research status of battery safety accidents of electric vehicles[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(24): 93-104,116. | |
| 53 | 中国汽车技术研究中心有限公司.EV-TEST(电动汽车测评)管理规则(2019版)[Z].2019. |
| China Automotive Technology and Research Center Co. Ltd. EV-TEST (electric vehicle evaluation) management rules (2019 edition) [Z]. 2019. | |
| 54 | 舒强,王艺帆,梁元.我国电动汽车动力电池安全标准现状及展望[J].汽车工程,2022,44(11):1706-1715. |
| SHU Q, WANG Y F, LIANG Y. Current situation and prospect of safety standard of electric vehicle power battery [J]. Automotive Engineering, 2022, 44(11): 1706-1715. | |
| 55 | 国家市场监督管理总局,中国国家标准化管理委员会.电动汽车用动力蓄电池安全要求: GB 38031—2020[S].北京:中国标准出版社,2020. |
| State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration of China. Safety requirements for power batteries for electric vehicles: GB 38031—2020[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2020. | |
| 56 | CHEN X B, WANG M Y, WANG W. Unified chassis control of electric vehicles considering wheel vertical vibrations[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(11): 3931. |
| 57 | 陈泽宇,张渤,熊瑞,等.动力电池低温极速自加热系统加热一致性及其影响因素的建模分析[J].机械工程学报,2021,57(22):226-236. |
| CHEN Z Y, ZHANG B, XIONG R, et al. Modeling and analysis of heating consistency and influencing factors of low-temperature ultra-fast self-heating system of power battery[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 57(22): 226-236. | |
| 58 | GABBAR H A, OTHMAN A M, ABDUSSAMI M R. Review of battery management systems (BMS) development and industrial standards[J]. Technologies, 2021, 9(2): 28. |
| 59 | 于东民,杨超,蒋林洳,等.电动汽车充电安全防护研究综述[J].中国电机工程学报,2022,42(6):2145-2164. |
| YU D M, YANG C, JIANG L R, et al. Review of research on electric vehicle charging safety protection [J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2022, 42(6): 2145-2164. | |
| 60 | 丁飞,张楠,李升波,等.智能网联车路云协同系统架构与关键技术研究综述[J].自动化学报,2022,48(12):2863-2885. |
| DING F, ZHANG N, LI S B, et al. Research review on architecture and key technologies of intelligent networked vehicle road cloud collaborative system [J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(12): 2863-2885. | |
| 61 | XUN Y J, LIU J J, ZHANG Y N. Side-channel analysis for intelligent and connected vehicle security: a new perspective[J]. IEEE Network, 2019, 34(2): 150-157. |
| 62 | GUAN T, HAN Y, KANG N, et al. An overview of vehicular cybersecurity for intelligent connected vehicles[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(9): 5211. |
| 63 | 中国软件评测中心.智能网联汽车安全渗透白皮书(3.0版)[EB/OL].[2023-3-20].https://www.cstc.org.cn/cpyj/jsbg/jsbps.htm. |
| China Software Test Center. Intelligent connected vehicle security penetration white paper (version 3.0)[EB/OL].[2023-3-20].https://www.cstc.org.cn/cpyj/jsbg/jsbps.htm. | |
| 64 | 中汽中心. C-ICAP中国智能网联汽车技术规程(1.0版)正式发布[EB/OL].[2022-12-30]. https://www.c-ncap.org.cn/article detail/1608635654437126146?type=2. |
| CAIC Center. C-ICAP China intelligent connected vehicle technical regulations (version 1.0) officially released[EB/OL].[2022-12-30].https://www.c-ncap.org.cn/article detail/160863565443 7126146?type=2. | |
| 65 | HE K X, CHANG Y W, HAN Y Y, et al. Research on cyber security technology and test method of OTA for intelligent connected vehicle[C]. 2020 International Conference on Big Data, Artificial Intelligence and Internet of Things Engineering (ICBAIE). IEEE, 2020: 194-198. |
| 66 | WU Z, LIU T Y, JIA X F, et al. Security design of OTA upgrade for intelligent connected vehicle[C]. Proceedings of the 2021 1st International Conference on Control and Intelligent Robotics, 2021: 736-739. |
| 67 | 韩嘉懿,赵健,朱冰.面向智能汽车人机协同转向控制的强化学习变阻抗人机交互方法[J].机械工程学报,2022, 58(18):141-149. |
| HAN J Y, ZHAO J, ZHU B. Variable impedance human-computer interaction based on reinforcement learning for intelligent vehicle collaborative steering control [J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 58(18): 141-149. | |
| 68 | 朱宇,赵祥模,李春银,等. 面向自动驾驶虚实结合测试的虚实交互系统设计与验证[C]. 中国科学技术协会,交通运输部,中国工程院,湖北省人民政府.2022世界交通运输大会(WTC2022)论文集(运输规划与交叉学科篇).人民交通出版社股份有限公司,2022:910-918. |
| ZHU Y, ZHAO X M, LI C Y, et al. Design and verification of virtual-real interaction system for virtual and real combined testing of autonomous driving[C]. China Association for Science and Technology, Ministry of Transport, Chinese Academy of Engineering, Hubei Provincial People's Government.2022 World Transportation Conference (WTC2022) Proceedings (Transportation Planning and Interdisciplinarity). People's Communications Press Co., Ltd., 2022: 910-918. | |
| 69 | ZHI P, ZHAO R, ZHOU H R, et al. Analysis on the development status of intelligent and connected vehicle test site[J]. Intelligent and Converged Networks, 2021, 2(4): 320-333. |
| 70 | WANG X Y, ZANG L G, WANG Z, et al. Study on the stability control of vehicle tire blowout based on run-flat tire[J]. World Electric Vehicle Journal, 2021, 12(3): 128. |
| [1] | 关书睿,李克强,周俊宇,石佳,孔伟伟,罗禹贡. 面向强制换道场景的智能网联汽车协同换道策略[J]. 汽车工程, 2024, 46(2): 201-210. |
| [2] | 王庞伟,刘程,汪云峰,张名芳. 面向城市道路的智能网联汽车多车道轨迹优化方法[J]. 汽车工程, 2024, 46(2): 241-252. |
| [3] | 刘济铮,王震坡,孙逢春,张雷. 异构智能网联汽车编队延迟补偿控制研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2023, 45(9): 1573-1582. |
| [4] | 吴思宇,于文浩,邢星宇,张玉新,李楚照,李雪轲,古昕昱,李云巍,马小涵,路伟,王政,郝圳茂,王红,李骏. 基于关键场景的预期功能安全双闭环测试验证方法[J]. 汽车工程, 2023, 45(9): 1583-1607. |
| [5] | 左政,王云鹏,麻斌,邹博松,曹耀光,杨世春. 基于AFC-TARA的车载网络组件风险率量化评估分析[J]. 汽车工程, 2023, 45(9): 1553-1562. |
| [6] | 李升波,占国建,蒋宇轩,兰志前,张宇航,邹文俊,陈晨,成波,李克强. 类脑学习型自动驾驶决控系统的关键技术[J]. 汽车工程, 2023, 45(9): 1499-1515. |
| [7] | 边有钢,张田田,谢和平,秦洪懋,杨泽宇. 车辆队列抗扰抗内切协同路径跟踪控制[J]. 汽车工程, 2023, 45(8): 1320-1332. |
| [8] | 朱冰,姜泓屹,赵健,韩嘉懿,刘彦辰. 智能网联汽车协同感知信任度动态计算与评价方法[J]. 汽车工程, 2023, 45(8): 1383-1391. |
| [9] | 关宇昕,冀浩杰,崔哲,李贺,陈丽文. 智能网联汽车车载CAN网络入侵检测方法综述[J]. 汽车工程, 2023, 45(6): 922-935. |
| [10] | 胡耘浩,李克强,向云丰,石佳,罗禹贡. 智能网联汽车通用跨平台实时仿真系统架构及应用[J]. 汽车工程, 2023, 45(3): 372-381. |
| [11] | 刘浩天,魏洪乾,时培成,张幽彤. 基于帧间隔-总线电压混合特征的汽车ECU伪装攻击识别[J]. 汽车工程, 2023, 45(11): 2070-2081. |
| [12] | 李捷,吴晓东,许敏,刘永刚. 基于强化学习的城市场景多目标生态驾驶策略[J]. 汽车工程, 2023, 45(10): 1791-1802. |
| [13] | 钱立军,陈晨,陈健,陈欣宇,熊驰. 基于Q学习模型的无信号交叉口离散车队控制[J]. 汽车工程, 2022, 44(9): 1350-1358. |
| [14] | 钟文沁,孔伟伟,李志恒,于杰,罗禹贡. 不同渗透率下非信控交叉路口混合预约多车协同控制[J]. 汽车工程, 2022, 44(8): 1144-1152. |
| [15] | 陈一鹤,孔伟伟,于杰,李克强,罗禹贡. 混合交通下非信控交叉口队列预约式控制[J]. 汽车工程, 2022, 44(7): 953-959. |
|